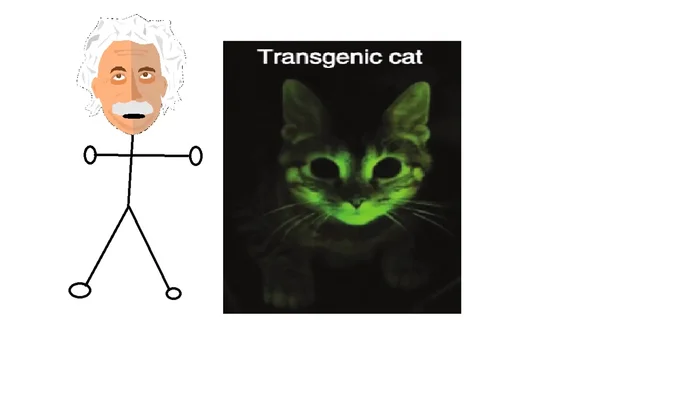
The idea of a cat that glows in the dark might sound like science fiction, but thanks to advancements in genetic engineering, it's a reality. For years, scientists have experimented with introducing fluorescent proteins into animals, resulting in some truly spectacular (and sometimes controversial) results. This process, while complex, offers a fascinating glimpse into the world of genetic modification and its potential applications. Beyond the novelty factor, the research involved in creating these luminous felines contributes valuable knowledge to fields like disease research and gene therapy.
This guide provides a comprehensive, albeit simplified, overview of the process involved in creating glow-in-the-dark cats. We'll walk you through each step, from selecting the appropriate genes to the final observation of fluorescence, offering insights into the intricate techniques and ethical considerations that accompany this groundbreaking scientific endeavor. Let's dive into the illuminating world of genetic engineering and uncover the step-by-step process.
Preparation and Safety Guidelines
- Jellyfish
- Micropipette
- Incubator
- Cat Egg
- Catheter
- This procedure is extremely complex and requires advanced genetic engineering expertise. Attempting this without the proper training and equipment is incredibly dangerous and unethical.
- The long-term health effects of genetically modifying cats to glow in the dark are unknown and could be detrimental to the animal's well-being. Consider the ethical implications before proceeding.
- Strict regulations govern genetic modification in most jurisdictions. Modifying a cat's genes without the proper licenses and approvals is illegal and carries severe penalties.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Gene Extraction
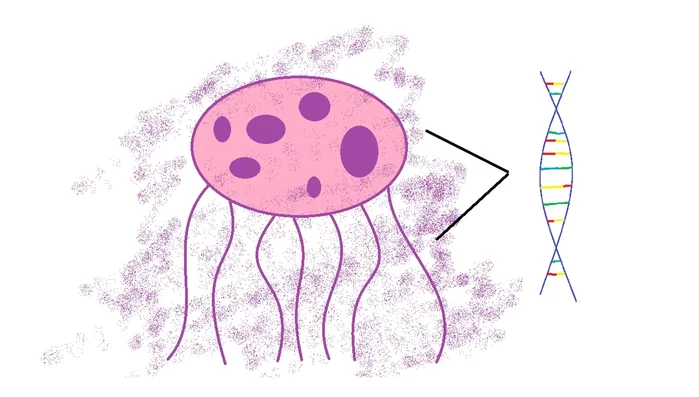
- Extract the bioluminescent gene from a jellyfish.

Gene Extraction Gene Insertion and Fertilization
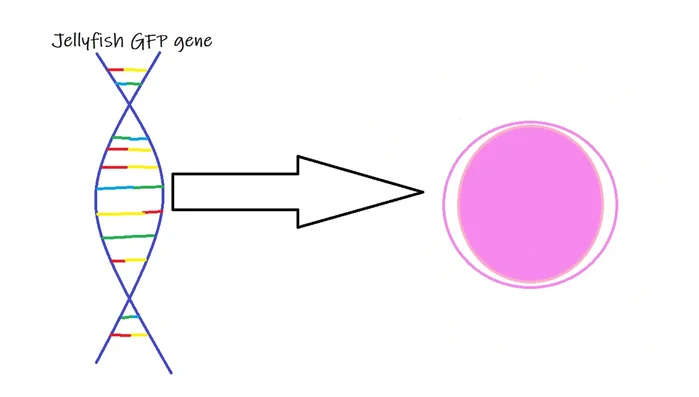
- Transgenically insert the gene into a cat egg (oocyte) using microinjection.
- Fertilize the egg through in vitro fertilization.


Gene Insertion and Fertilization Surrogate Pregnancy
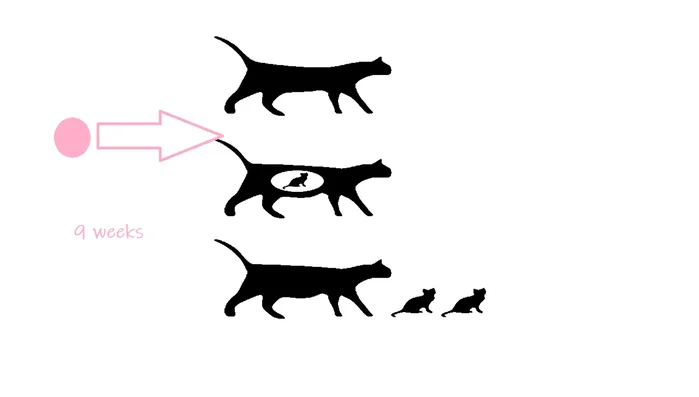
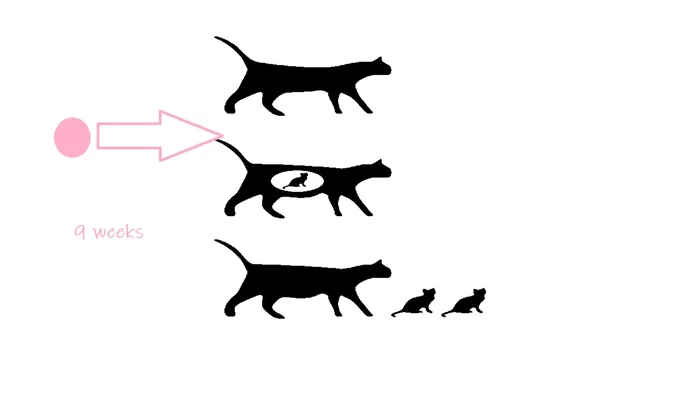
- Insert the fertilized egg into a surrogate cat.
- Wait for a nine-week gestation period.


Surrogate Pregnancy Bioluminescent Kitten
- The resulting kitten will be bioluminescent.

Bioluminescent Kitten
Read more: No-Sew Sock Cat Tutorial: Adorable DIY Project
Tips
- N/A